From production to warehouse management to the transport of manufactured goods – digitalisation is fundamentally changing the logistics process. It is indispensable that today’s logistics centres rely on comprehensive networking in order to optimally prepare for the future.
Implement transparent processes in logistics
E-commerce, smart factory and just-in-time deliveries require transparency in supply chain management. Ultimately, this is also important for the end customer, who orders goods from manufacturers and suppliers all over the world and wants to be able to see where his delivery is at any time. However, in order for digitalisation in logistics to advance, logistics companies must optimise their processes and develop new business models in order to remain competitive. As part of this development, new platforms are emerging that connect people, machines and data. This also having a clear impact on the logistics industry, especially with regard to flexibility, speed and the traceability of individual processes. Logistics 4.0 is thus becoming increasingly important for companies that want to continue to position themselves successfully.
Logistics 4.0 describes an application area of Industry 4.0 in which the technologies of digitalised industry are incorporated into logistics. Supply Chain 4.0 maps the integration and networking of objects, processes, dealers and suppliers as well as customers and manufacturers.
The basis of Logistics 4.0 are objects and processes that are able to organise and control themselves. For example, GPS technology can be used for localisation, RFID chips, barcodes and sensors for identification. Electronic and automated data transmission takes place via cloud-based services. The entire system is then an intelligent solution whose individual components communicate with each other via the Internet of Things (IoT) and use AI to learn from each other, make decisions and monitor themselves.
Challenges of digitalisation: rethinking old processes
For many people, the constant use of smartphones, tablet PCs and notebooks is now part of everyday life. This has also radically changed buying behaviour. Demand generation and fulfilment takes place predominantly online. This also increases the need for optimised service and product customisation. An item in an online department stores’ can be ordered with just a few mouse clicks or finger taps, and logistics companies have to adjust to this.
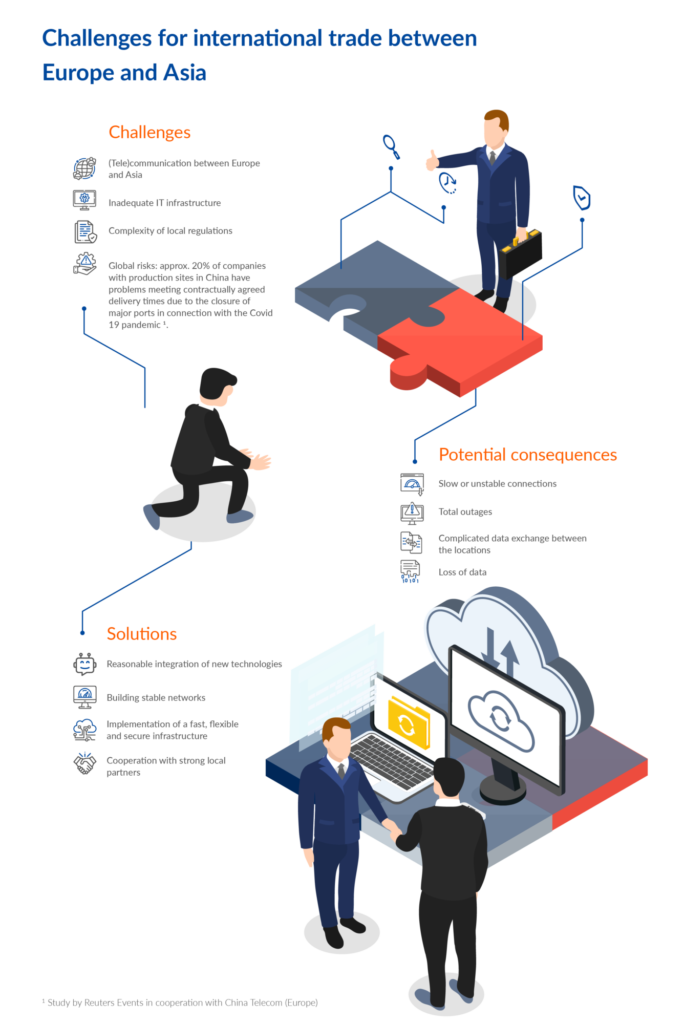
Summarised, this means: Old processes have to be rethought. The massive growth in data volume also increases the complexity of all processes and information involved. Trained employees in the company who can cope with this complexity are needed here. Last but not least, a restructuring of the work organisation is also necessary here, especially since people, machines, devices and robots now no longer just complement each other, but work together.
Solutions and innovations in logistics
Modern transport requires intelligent information and communication technologies. Technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, augmented reality, the 5G mobile communications standard and the Internet of Things (IoT) are worth mentioning here.
Supply Chain Technology: Key Trends and Technologies
5G is a mobile communications standard that will gain in importance in the future. It is the successor to the currently common LTE standard and, in addition to the usual telephony and general internet access, enables many devices to be networked with each other with little energy expenditure and low latency as part of the Internet of Things.
Internet of Things (IoT) comprises technologies that connect physical and virtual objects globally. Here, the IPv6 standard allows literally every object to have its own IP address, enabling it to communicate and collaborate with any other object of its own class, regardless of location.
Big Data refers to data volumes that are so large and/or complex that they can no longer be analysed and processed using conventional IT means. Cloud technologies, artificial intelligence and broadband data networks help to cope with the volume of data.
Blockchain is a technology that has become known from the environment of cryptocurrencies (e.g. Bitcoin). A blockchain is a decentralised database distributed across several computers on which bookings, smart contracts, etc. can be stored. The blockchain is characterised by book-secure data security, because each individual data record builds on the previous and subsequent data records and thus cannot be falsified.
Augmented reality stands for technologies that make it possible to display additional information besides the actual visually perceivable environment. This process has become known through data glasses, which, for example, display supplementary information in an unfamiliar environment. However, this also works with conventional visual devices, for example during a football broadcast on television, where additional lines or distances between two points are superimposed on the playing field. This technology can also be used to benefit logistical processes.
In logistics there are solutions already available today that, with the help of hardware and software, can trace, analyse and, if necessary, optimise a complete supply chain from the manufacturer to the end customer. For example, if a transport route is not available and alternatives have to be sought. However, the prerequisite is always a reliable connectivity of all components involved. Only a competent provider can guarantee this.
Opportunities of digitalisation in logistics
Digitalised business models have permanently changed the contact with the customer. In the past, a customer’s freight was picked up by the freight forwarder, who then organised the onward transport. Nowadays, digital platforms give every manufacturer, retailer or end consumer the opportunity to tender transport services for each individual consignment in direct competition. In this way, the transport clients have direct contact with the logistics providers and thus achieve greater transparency.
This transparency not only results in satisfied customers, but also in a number of other benefits that ensure the success and competitiveness of your company and result directly from the optimisations of all processes, for example:
- optimal work results thanks to ongoing optimisations
- reduced costs and conservation of resources thanks to comprehensive analyses
- Error prevention thanks to automation
Meeting the trends of the future
The digital transformation is not a project that will be completed at some point, but a holistic process that is constantly learning and adapting to new requirements and individual circumstances. In today’s times of continuous change and new requirements for scalable systems, Logistics 4.0 offers invaluable potential for companies to continuously optimise logistics performance and improve competitiveness. Some points will become even more important in the future:
Fulfilling individual customer requirements
Customised production and delivery are becoming increasingly important. By means of Logistics 4.0, special customer wishes can be realised even with the smallest batch sizes. Automated and transparent processes as well as networking enable companies of all sizes to implement decision-making and control processes in a decentralised manner using existing data and adaptive AI algorithms.
Enabling fast deliveries
Both logistics service providers and manufacturing companies will share warehouse space, transports, distribution centres and also reverse logistics chains through networked technologies in the course of Logistics 4.0. This will create global logistics super-networks that enable significantly faster deliveries. In addition, web-based “Logistics as a Service” and virtual logistics marketplaces are emerging through the Internet of Things.
Ensuring data protection
Digitalised logistics poses major challenges for companies that use it. Due to the extremely large amounts of data, data protection is becoming a core component of Logistics 4.0 in accordance with the EU Data Protection Regulation. Solutions must be created here that guarantee the security of personal and company-related data. Blockchain-based applications are the modern means of choice here. In many medium-sized logistics companies, fear of cyber attacks is considered an obstacle to the introduction of digital infrastructures. Yet companies can do a great deal to secure their data networks with reliable partners, which ultimately also ensures a positive external image towards customers. Here, you should involve security experts in the digitalisation process and additionally sensitise employees to security awareness.
Conclusion
For Logistics 4.0, functioning and stable connectivity is a mandatory prerequisite – regardless of whether it is wired or wireless. In our “The Future of Global Supply Chains: New Technologies in Supply Chain Management” report, you will find further details on relevant topics of interest in the course of global supply chains, including activities and challenges of the Chinese market and the Asia-Pacific region, Internet of Things, cloud technology as well as cyber security.

As a professional telecommunications service provider, China Telecom (Europe) is your reliable partner when it comes to planning and building global data networks. We are there for you throughout Europe at 21 locations – also in your national language.















 Return to Blogs & Related News
Return to Blogs & Related News

